Link-State ID是路由器、Link ID是路由器網路卡。我在CCIE RS v5.0這本書看到這個內容,作者是Narbik Kocharians - CCIE #12410、Peter Palúch - CCIE #23527。
我們必須先精通OSPF LSA封包的型別,才有能力區別兩者的不同。因為OSPF網路是基於區域(area)的概念,才設計出各種相應區域的LSA型別。所有LSA型別的內容有長有短,然而除了type 1 LSA,都有2個關鍵的相同點:所有LSA都是從type 1延伸、所有LSA都描述到達目的地網路與其下一站是誰(類似設定靜態路由)。
Type 1 LSA(router)
此型別定義了自己是誰、有幾條OSPF連接、每條OSPF連接的成本。
Type 2 LSA(network)
此型別紀錄了DR存在的網段有多少OSPF路由器(鄰居關係為full)、與它們的路由器ID。
若某個網段僅使用type 1 LSA同步資料庫則會造成一個問題,當R1、R2、R3位於相同網段,R1是DR,R2、R3會將R1當作下一站,而非從R2直接轉發到R3;所以type 2 LSA紀錄網段內所有OSPF路由器。使同步後的DRother不用經過DR。
因為OSPF點對點網路類型不用選DR/BDR,所以收斂速度比廣播還要快上許多。

Type 3 LSA(summary)
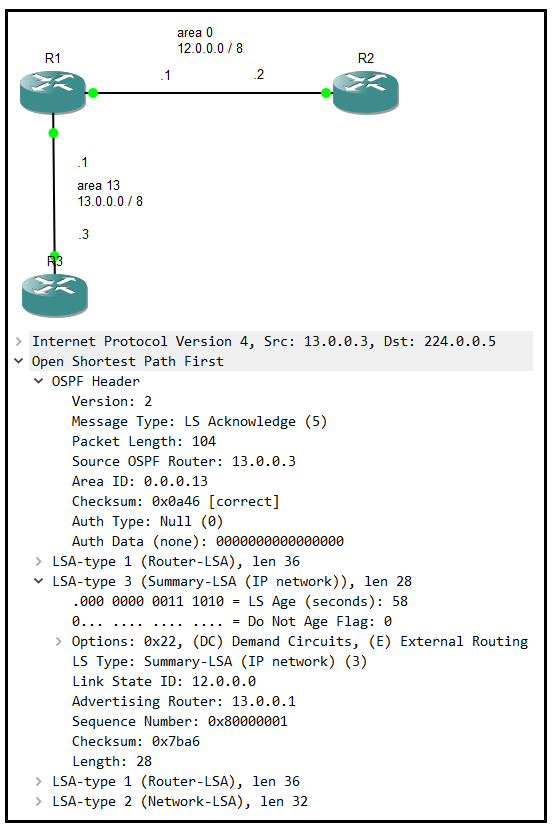
此型別用來通告一般區域(area 13)的路由器(R3)如何抵達骨幹區域(area 0)的路由器(R2);反之亦然。
並且type 1、type 2 LSA不能跨區域轉發,由type 3 LSA整合描述type 1、type 2。
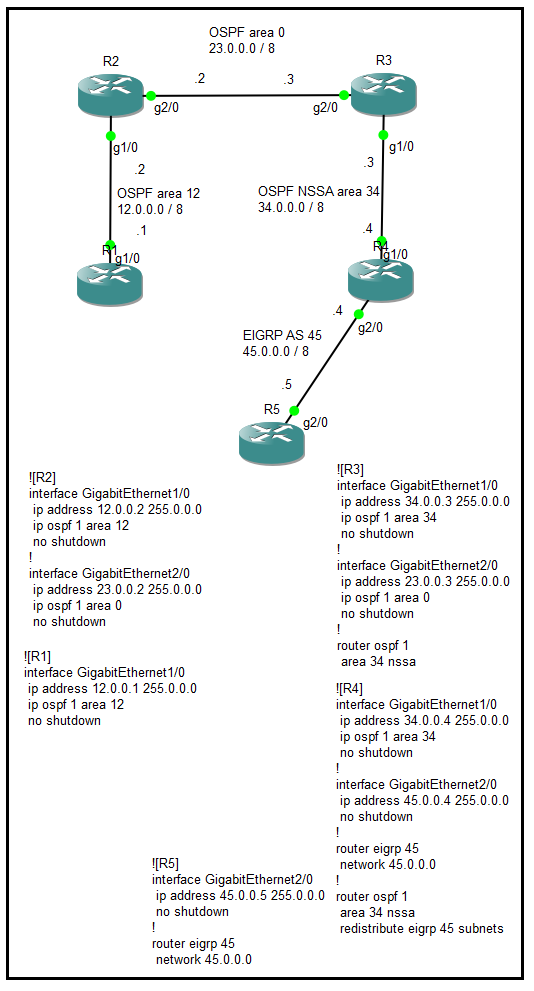
Type 4 LSA(ASBR summary)
此型別像Type 3 LSA,也是由ABR(R2)產生,主要用來通告一般區域(area 12)內的路由器(R1)如何抵達AS外部區域(EIGRP AS 34)。

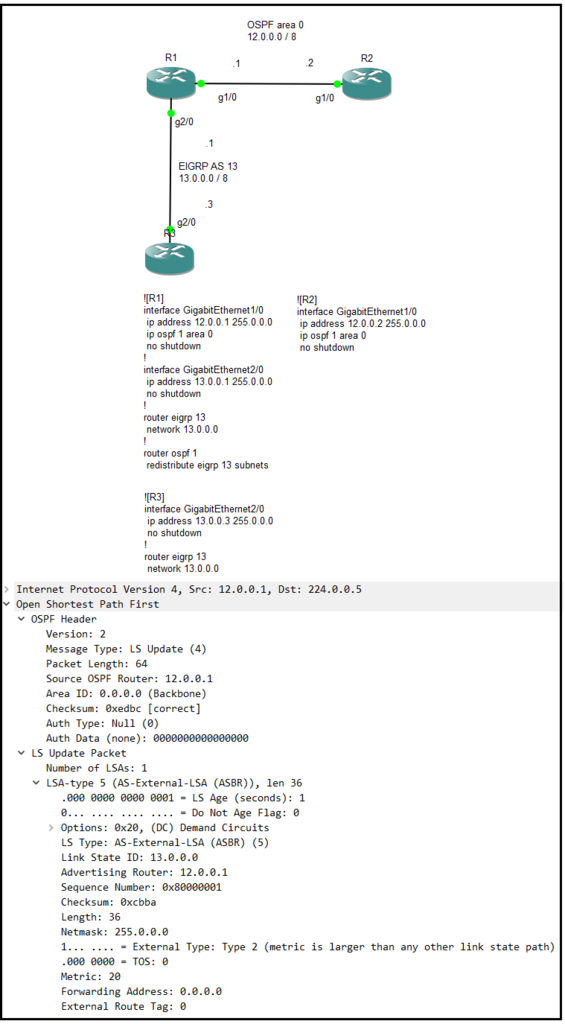
Type 5 LSA(AS external)
此型別由ASBR(R1)產生,用來告訴OSPF路由器(R2)如何抵達AS外部區域(EIGRP AS 13)。
Type 7 LSA(NSSA external)
此型別由NSSA區域的ASBR(R3)產生,用來通告NSSA區域(area 34)的路由器(R3)如何抵達外部AS區域(EIGRP AS 45)。
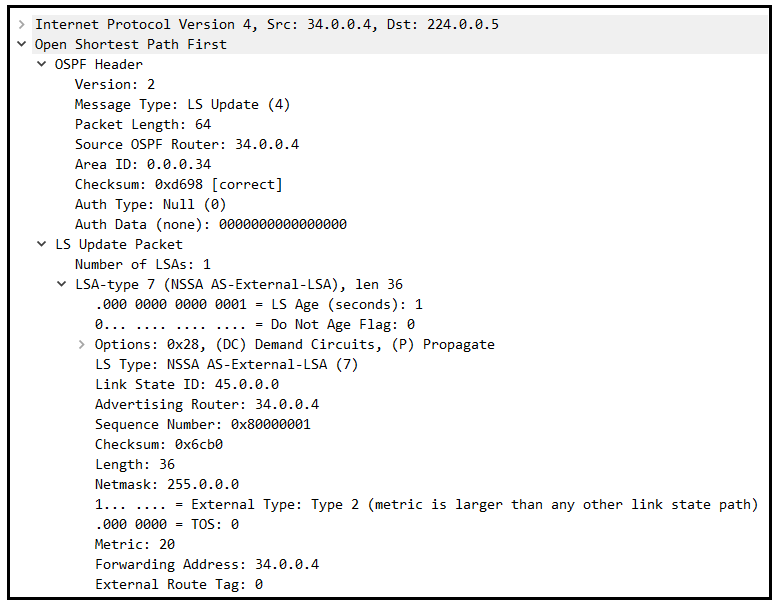

Type 4與type 5 LSA很像,相同點都是通告給OSPF路由器如何抵達外部AS區域。相異點是type 4 LSA由ABR產生、type 5由ASBR產生。
Type 5與type 7 LSA很像,相同點都是由ASBR產生,相異點是type 5 LSA在所有OSPF區域沖刷(末端區域除外),也是唯一可跨越所有區域的LSA型別;但type 7 LSA僅在NSSA區域沖刷,並由ABR轉換為type 5 LSA。
接著我們進入此文章之重點。我節錄CCIE RS v5.0中OSPF部分段落內容:「Be aware of a long-term glitch in the show ip ospf database output: The Link ID column is a misnomer; correctly, it should say Link State ID. This seemingly subtle difference is serious enough to warrant a mention: While Link State ID is a unique identifier of an entire LSA, a Link ID is a particular entry specifically in a type 1 LSA body that describes an adjacency to a neighboring object of a router. A single type 1 LSA identified by a single Link State ID can describe several adjacencies represented by several Link ID entries. These two terms are not interchangeable. 」
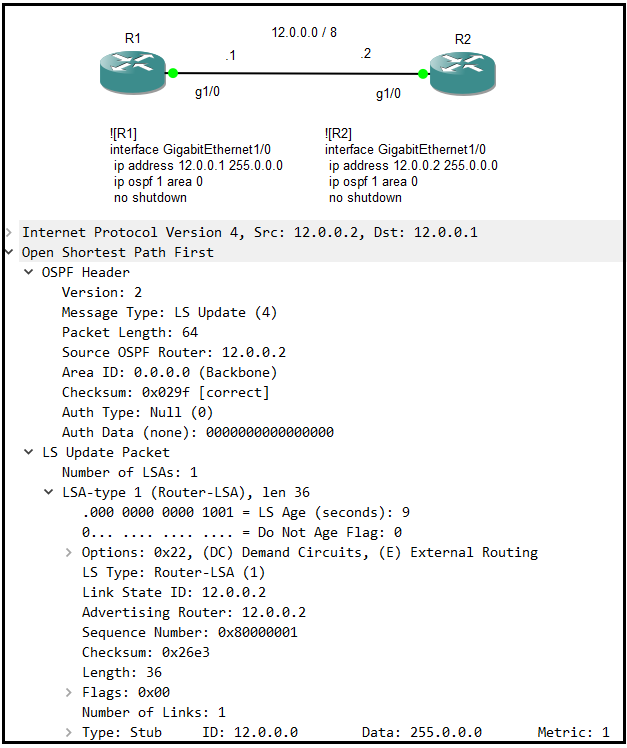
請參考下方拓樸與配置


命令「show ip ospf database」的輸出內容中,欄位「Link ID」被認為是不正確的,正確為「Link-State ID」,這是設計上的錯誤但不影響系統運作。
命令「show ip ospf database network 13.0.0.3」的輸出內容中,可以看到其中一行寫著Link-State ID為13.0.0.3,它是DR地址。
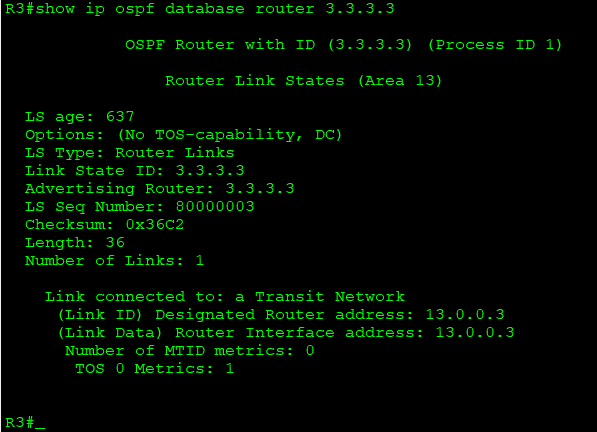
命令「show ip ospf database router 3.3.3.3」的輸出內容中,可以看到R3的Link-State ID為3.3.3.3、Link ID為13.0.0.3。
Link-State ID is router, Link ID is interface of router. I saw this content at CCIE RS v5.0 . The book writers are Narbik Kocharians - CCIE #12410, Peter Palúch - CCIE #23527.
First, we are must proficient in OSPF LSA types, be have ability to distinguish them. Because OSPF network is concept of area-based, be design LSA types of various corresponding area.
The LSA types content are big or small, but except type 1 LSA, they have 2 crucial same content: all LSA are extend from type 1; All LSA are descript how to arrive destination network and who is next hop(similar to set static route).
Type 1 LSA(router)
The type defined who am me? How many OSPF connection, and their cost.
[image]
Type 2 LSA(network)
The type records how many OSPF routers at network where DR exist, and their router ID.
If some network use type 1 LSA only to synchronize OSPF database that cause a problem. When R1, R2 and R3 at same network, and R1 is DR. The R2 and R3 are taken R1 as next hop, not forward R3 from R2.
So type 2 LSA records every OSPF router in network, make synchronized DRothers are not need through DR.
OSPF point-to-point network type has not need elect DR/BDR, so convergence speed is very quick than broadcast.
[image]
Type 3 LSA(summary)
The type used advertise router(R3) at standard area(area 13) how to arrive router(R2) at backbone area(area 0); vice versa.
And type 1, type 2 LSA can not forwarding through area. By type 3 LSA, integrate descript type 1, type 2.
[image]
Type 4 LSA(ASBR summary)
The type is like type 3, also generate by ABR(R2). It is mainly used advertise router(R1) at standard area(area 12) how to arrive AS of external(EIGRP AS 34).
[image]
Type 5 LSA(AS external)
The type is generate by ASBR(R1), it used notice OSPF router(R2) how to arrive AS of external(EIGRP AS 13).
[image]
Type 7 LSA(NSSA external)
The type is generate by ASBR(R3) at NSSA area, it used advertise router(R3) at NSSA area(area 34) how to arrive AS of external(EIGRP AS 45).
[image]
Type 4 and type 5 LSA are like, their same is advertise routing for OSPF router how to arrive external AS area. Their difference that type 4 LSA is generate by ABR, type 5 by ASBR.
Type 5 and type 7 LSA are like, their same is generate by ASBR. Their difference that type 5 LSA be flood at every OSPF area(except stubby area). It is also LSA type that through all areas only;
But type 7 LSA has flood at NSSA area only, and translate type 5 LSA by ABR.
And then, we have enter main of this writing. I excerpt some section content from CCIE RS v5.0:「Be aware of a long-term glitch in the show ip ospf database output: The Link ID column is a misnomer; correctly, it should say Link State ID. This seemingly subtle difference is serious enough to warrant a mention: While Link State ID is a unique identifier of an entire LSA, a Link ID is a particular entry specifically in a type 1 LSA body that describes an adjacency to a neighboring object of a router. A single type 1 LSA identified by a single Link State ID can describe several adjacencies represented by several Link ID entries. These two terms are not interchangeable.」
Please refer topology and configuration below
[image]
[image]
The output content of command 「show ip ospf database」, that column 「Link ID」 was not correct. 「Link-State ID」 is correctly, it is error for design but not effect working for system.
The output content of command 「show ip ospf database network 13.0.0.3」, you can see some line that mean Link-State ID is 13.0.0.3. It is address of DR.
[image]
The output content of command 「show ip ospf database router 3.3.3.3」, you can see Link-State ID of R3 is 3.3.3.3 .




 留言列表
留言列表


